ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers
本课程是吴恩达与OpenAI、Hugging Face、LangChain等机构联合打造,面向开发者的LLM系列课程第一讲——面向开发者的ChatGPT Prompt Engineering,由OpenAI的Isa Fulford和吴恩达合作授课。
课程链接
ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers
建议大家直接看DeepLearning.AI上的英文原版,配合官方提供的Jupyter Notebook效果更佳。B站上的翻译稀烂,不建议看,可能会造成误导。
友情提示:Isa的语速超快,还是英国口音,real难懂,实在听不懂就降低倍速吧。
概述
在自然语言处理和人工智能领域,Prompt是指提供给模型(特别是语言模型,如GPT-3、GPT-4、BERT等)的一段输入文本,用来引导模型进行特定任务的生成或推理。它是模型与用户之间的桥梁,用户通过设计合适的Prompt来获取所需的输出。Prompt Engineering(提示工程)指设计、优化和调整输入提示以便引导模型生成所需的输出。
在本课程中,你将学习如何使用LLM快速构建新的强大的应用程序。Isa Fulford和吴恩达将描述LLM的工作原理,提供Prompt Engineering的最佳实践,并将LLM api应用在总结(例如,为简洁而总结用户评论)、推断(例如,情感分类,主题提取)、转换文本(例如,翻译,拼写和语法纠正)和扩展(例如,自动写电子邮件)任务上。
此外,你将学习编写有效prompt的两个原则,如何系统的设计好的prompt以及如何自定义聊天机器人。
Prompting Principles
- Principle 1: 编写明确具体的指令;
- Principle 2: 给模型时间去思考;
下面分别介绍每个principle使用的具体策略。
Principle 1
策略1:使用分隔符清楚地表示输入的不同部分,例如```, “””, <>,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
text = f"""
You should express what you want a model to do by \
providing instructions that are as clear and \
specific as you can possibly make them. \
This will guide the model towards the desired output, \
and reduce the chances of receiving irrelevant \
or incorrect responses. Don't confuse writing a \
clear prompt with writing a short prompt. \
In many cases, longer prompts provide more clarity \
and context for the model, which can lead to \
more detailed and relevant outputs.
"""
prompt = f"""
Summarize the text delimited by triple backticks \
into a single sentence.
```{text}```
"""
要总结的文本text用三个反引号`{text}\`分隔开来。
策略2:要求模型输出结构化数据,例如JSON、HTML。
1
2
3
4
5
6
prompt = f"""
Generate a list of three made-up book titles along \
with their authors and genres.
Provide them in JSON format with the following keys:
book_id, title, author, genre.
"""
在prompt中明确要求模型输出’in JSON format’。
策略3:请模型检查是否满足条件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
text_1 = f"""
Making a cup of tea is easy! First, you need to get some \
water boiling. While that's happening, \
grab a cup and put a tea bag in it. Once the water is \
hot enough, just pour it over the tea bag. \
Let it sit for a bit so the tea can steep. After a \
few minutes, take out the tea bag. If you \
like, you can add some sugar or milk to taste. \
And that's it! You've got yourself a delicious \
cup of tea to enjoy.
"""
prompt = f"""
You will be provided with text delimited by triple quotes.
If it contains a sequence of instructions, \
re-write those instructions in the following format:
Step 1 - ...
Step 2 - …
…
Step N - …
If the text does not contain a sequence of instructions, \
then simply write \"No steps provided.\"
\"\"\"{text_1}\"\"\"
"""
如果text中包含一系列的指令,按照以下格式重写这些指令。否则,输出No steps provided.
Step 1 - …
Step 2 - …
…
Step N - …
策略4:“Few-shot” prompting。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
prompt = f"""
Your task is to answer in a consistent style.
<child>: Teach me about patience.
<grandparent>: The river that carves the deepest \
valley flows from a modest spring; the \
grandest symphony originates from a single note; \
the most intricate tapestry begins with a solitary thread.
<child>: Teach me about resilience.
"""
在prompt中先提供少量的例子给模型,然后再向模型提问。
Principle 2
策略1:指定完成任务所需的步骤。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
text = f"""
In a charming village, siblings Jack and Jill set out on \
a quest to fetch water from a hilltop \
well. As they climbed, singing joyfully, misfortune \
struck—Jack tripped on a stone and tumbled \
down the hill, with Jill following suit. \
Though slightly battered, the pair returned home to \
comforting embraces. Despite the mishap, \
their adventurous spirits remained undimmed, and they \
continued exploring with delight.
"""
# example 1
prompt_1 = f"""
Perform the following actions:
1 - Summarize the following text delimited by triple \
backticks with 1 sentence.
2 - Translate the summary into French.
3 - List each name in the French summary.
4 - Output a json object that contains the following \
keys: french_summary, num_names.
Separate your answers with line breaks.
Text:
```{text}```
"""
Perform the following actions: 明确指出模型需要执行的操作。
策略2:让模型得出答案前先给出解决方案。
这跟人类的行为很相似。假如让你解一道复杂的数学题,根据题干就直接给出答案是很困难的,往往不能得到正确答案。如果先分析问题,给出问题的解决方案,然后再根据方案求解答案,正确率能提高不少。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
prompt = f"""
Determine if the student's solution is correct or not.
Question:
I'm building a solar power installation and I need \
help working out the financials.
- Land costs $100 / square foot
- I can buy solar panels for $250 / square foot
- I negotiated a contract for maintenance that will cost \
me a flat $100k per year, and an additional $10 / square \
foot
What is the total cost for the first year of operations
as a function of the number of square feet.
Student's Solution:
Let x be the size of the installation in square feet.
Costs:
1. Land cost: 100x
2. Solar panel cost: 250x
3. Maintenance cost: 100,000 + 100x
Total cost: 100x + 250x + 100,000 + 100x = 450x + 100,000
"""
本例让模型(gpt-3.5-turbo)直接判断学生的答案是否正确。事实上,学生的答案是错误的,但是模型却认为是正确的。
我们让模型(gpt-3.5-turbo)先给出自己的解决方案和答案,然后再跟学生的解法做对比。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
prompt = f"""
Your task is to determine if the student's solution \
is correct or not.
To solve the problem do the following:
- First, work out your own solution to the problem including the final total.
- Then compare your solution to the student's solution \
and evaluate if the student's solution is correct or not.
Don't decide if the student's solution is correct until
you have done the problem yourself.
Use the following format:
Question:
```
question here
```
Student's solution:
```
student's solution here
```
Actual solution:
```
steps to work out the solution and your solution here
```
Is the student's solution the same as actual solution \
just calculated:
```
yes or no
```
Student grade:
```
correct or incorrect
```
Question:
```
I'm building a solar power installation and I need help \
working out the financials.
- Land costs $100 / square foot
- I can buy solar panels for $250 / square foot
- I negotiated a contract for maintenance that will cost \
me a flat $100k per year, and an additional $10 / square \
foot
What is the total cost for the first year of operations \
as a function of the number of square feet.
```
Student's solution:
```
Let x be the size of the installation in square feet.
Costs:
1. Land cost: 100x
2. Solar panel cost: 250x
3. Maintenance cost: 100,000 + 100x
Total cost: 100x + 250x + 100,000 + 100x = 450x + 100,000
```
Actual solution:
"""
模型(gpt-3.5-turbo)判定学生的答案是错误的,并给出正确解法。
这个策略对gpt-3.5-turbo是有效的,但是gpt-4不需要使用这个策略就能自动输出解题过程和正确答案。
模型的局限性:幻觉(Hallucinations)
语言模型产生的答案是靠“文字接龙”接出来的,模型并不知道这些“知识”,也不能判断这些“知识”是不是符合现实情况的。如果我们基于虚假的信息向模型提问,它也能产生”像模像样”的答案,这种现象被称为模型的幻觉。
1
2
3
prompt = f"""
Tell me about AeroGlide UltraSlim Smart Toothbrush by Boie
"""
‘Boie’公司是不存在,但是模型(gpt-3.5-turbo)却煞有介事的介绍起了产品。
我们拿同样的prompt去问gpt-4,gpt-4会告诉我们’Boie’公司和’AeroGlide UltraSlim Smart Toothbrush’都是不存在的。
Iterative Prompt Development
在开发应用时,很难通过第一次尝试就得到完美的prompt。如下图所示,需要进行多次迭代优化才能不断改进。
具体地,首先编写初始prompt,观察模型生成的结果是否满足需求;如果不理想,使用两个Principle改进prompt,再次尝试运行。如此循环多次,直到找到合适的prompt。
通过产品说明书生成营销产品描述:Generate a marketing product description from a product fact sheet
从初始prompt开始,逐步解决了3个issue(Issue 1: The text is too long、Issue 2. Text focuses on the wrong details、Issue 3. Description needs a table of dimensions),最终获得满足需求的prompt。
Summarizing
使用LLM对文本作摘要,从复杂的文本中快速提取出关键点。
概括电商平台评论:Summarizing
客户为一款熊猫公仔进行了点评,评价内容包括商品的质量、大小、价格和物流速度等因素,以及他的女儿对该商品的喜爱程度。通过编写不同的prompt,可以限制生成文本长度<30字、提取信息时有侧重(例如快递服务、价格与质量)。使用提取(extract)而非概括(summarize)可以滤掉其他无关信息,只保留某一方面的信息。调用OpenAI的API接口能够同时总结多个文本。
Inferring
与传统机器学习不同,使用LLM完成情感推断、信息提取、主题推断等任务,只需编写不同的prompt,不必单独为每个任务训练不同模型。
从产品评论和新闻文章中推断情绪和主题:Inferring
Transforming
大语言模型具有强大的文本转换能力,可以实现多语言翻译、拼写纠正、语法调整、格式转换等不同类型的文本转换任务。利用语言模型进行各类转换是它的典型应用之一。
使用LLM进行文本转换任务:Transforming
Expanding
文本扩展是大语言模型的一个重要应用方向,输入简短文本,生成更加丰富的长文。
根据每个客户评论生成电子邮件:Expanding
Chatbot
使用LLM构建chatbot(聊天机器人)进行多轮对话。
chatgpt APIopenai.ChatCompletion.create调用gpt-3.5-turbo,输入数据是包含多个dict的list:
1
2
3
4
5
[
{'role':xxx, 'content':xxxxxx},
{'role':xxx, 'content':xxxxxx},
......
]
‘role’有三个选项:
- system(系统):聊天系统的控制层面,它通常用于发送关于会话流程、规则设定、功能说明或技术性的信息;
- user(用户):与聊天机器人交互的人类用户;
- assistant(助手):聊天机器人本身。
‘content’:role发送的具体信息。一个典型的message类似这样:
1
2
3
4
5
messages = [
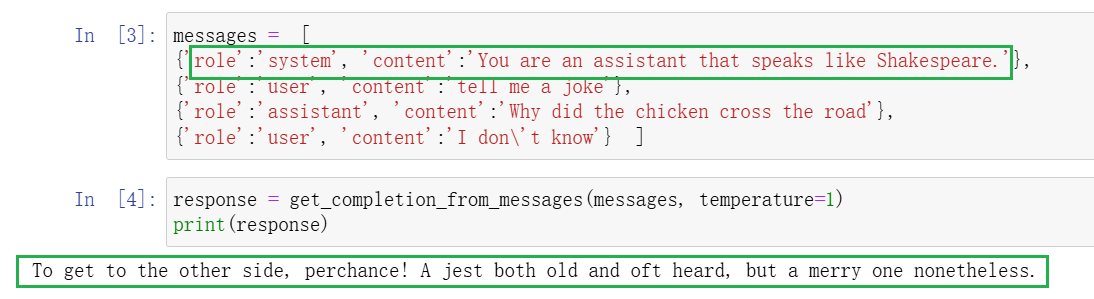
{'role':'system', 'content':'You are an assistant that speaks like Shakespeare.'},
{'role':'user', 'content':'tell me a joke'},
{'role':'assistant', 'content':'Why did the chicken cross the road'},
{'role':'user', 'content':'I don\'t know'} ]
给定角色
要构建不同身份的chatbot,我们以系统身份发送系统消息,设置chatbot的角色。
通过系统消息来定义:”你是一个说话像莎士比亚的助手“,助手的回答也是莎士比亚风格的。
构建上下文
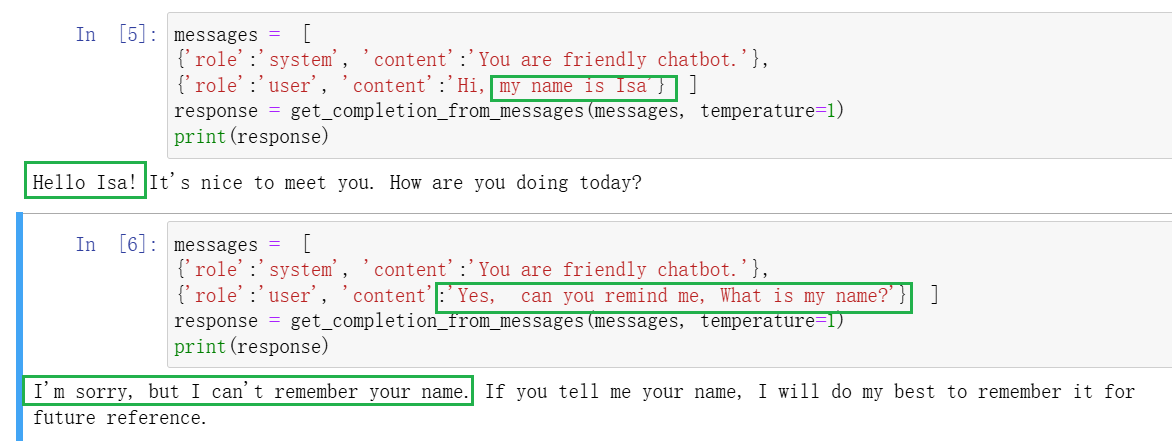
我们连续向模型提问两次,首先告诉模型’my name is Isa ‘,紧接着问模型’What is my name?’,但是模型并不记得my name。这是因为每次跟语言模型的交互都是独立的,如果想让模型“记住”早期的对话,必须在messages中提供早期的对话内容,即上下文(context)。
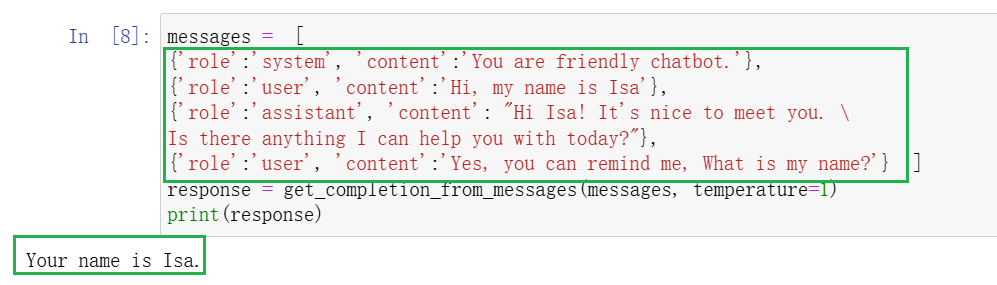
我们给模型提供完整的上下文,然后问’What is my name?’,模型知道’Your name is Isa.’。
OrderBot
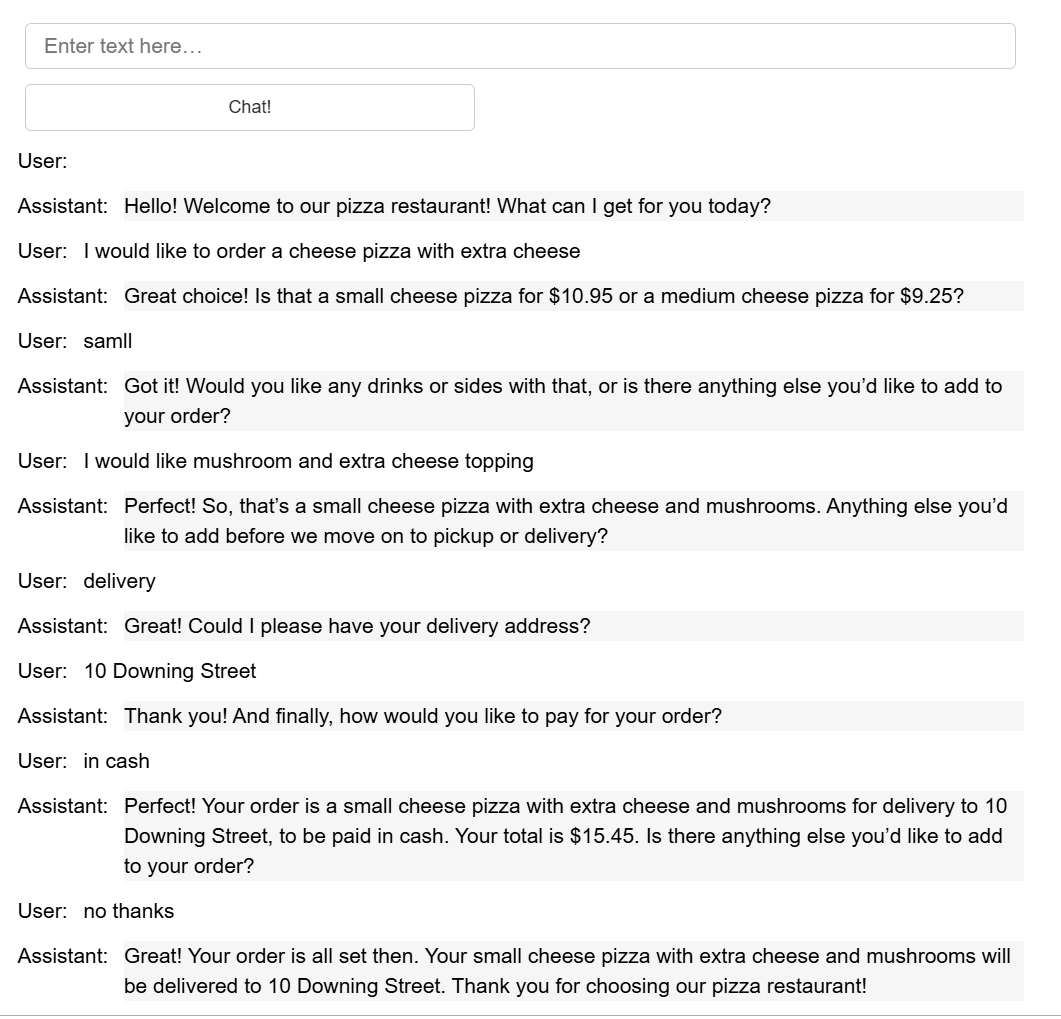
自动收集用户prompt和模型响应构建OrderBot(点餐机器人)。
def collect_messages(_)使用列表context收集完整上下文。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def collect_messages(_):
prompt = inp.value_input
inp.value = ''
context.append({'role':'user', 'content':f"{prompt}"})
response = get_completion_from_messages(context)
context.append({'role':'assistant', 'content':f"{response}"})
panels.append(
pn.Row('User:', pn.pane.Markdown(prompt, width=600)))
panels.append(
pn.Row('Assistant:', pn.pane.Markdown(response, width=600, style={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'})))
return pn.Column(*panels)
使用panel可视化界面。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
import panel as pn # GUI
pn.extension()
panels = [] # collect display
context = [ {'role':'system', 'content':"""
You are OrderBot, an automated service to collect orders for a pizza restaurant. \
You first greet the customer, then collects the order, \
and then asks if it's a pickup or delivery. \
You wait to collect the entire order, then summarize it and check for a final \
time if the customer wants to add anything else. \
If it's a delivery, you ask for an address. \
Finally you collect the payment.\
Make sure to clarify all options, extras and sizes to uniquely \
identify the item from the menu.\
You respond in a short, very conversational friendly style. \
The menu includes \
pepperoni pizza 12.95, 10.00, 7.00 \
cheese pizza 10.95, 9.25, 6.50 \
eggplant pizza 11.95, 9.75, 6.75 \
fries 4.50, 3.50 \
greek salad 7.25 \
Toppings: \
extra cheese 2.00, \
mushrooms 1.50 \
sausage 3.00 \
canadian bacon 3.50 \
AI sauce 1.50 \
peppers 1.00 \
Drinks: \
coke 3.00, 2.00, 1.00 \
sprite 3.00, 2.00, 1.00 \
bottled water 5.00 \
"""} ] # accumulate messages
inp = pn.widgets.TextInput(value="Hi", placeholder='Enter text here…')
button_conversation = pn.widgets.Button(name="Chat!")
interactive_conversation = pn.bind(collect_messages, button_conversation)
dashboard = pn.Column(
inp,
pn.Row(button_conversation),
pn.panel(interactive_conversation, loading_indicator=True, height=300),
)
dashboard
运行上面的代码可以得到一个点餐机器人,下图展示了点餐的交互过程:
Conclusion
本课程首先介绍了编写好的prompt的两个准则:编写明确具体的指令和给模型时间去思考。然后,给出编写好的prompt的迭代方法并展示了如何使用LLM完成文本摘要、推断、转化和扩展任务。最后介绍如何构建一个多轮对话聊天机器人。